japanese beetle life cycle colorado
Scientists and experts were caught off guard by the ability of the pest to establish itself in our region thinking that Japanese beetle an insect that likes moisture and humidity would never become a problem in the semi-arid Colorado climate. Adults usually emerge in June.

How To Protect Your Trees And Shrubs From Japanese Beetle Damage
The Japanese Beetle is a very common lawn pest that can be found in many different types of grasses all throughout the eastern part of the United States and as far west as Nebraska.

. The Japanese beetle was first introduced into Colorado in the early 1990s from nursery stock purchased in the mid-western United States. Japanese beetles go through a one-year life cycle but if you have a yard you care about the real joy with beetles comes in the second half of the summer in Colorado. In Colorado adult beetles emerge from the soil mid to late June with peak emergence occurring in mid to late July.
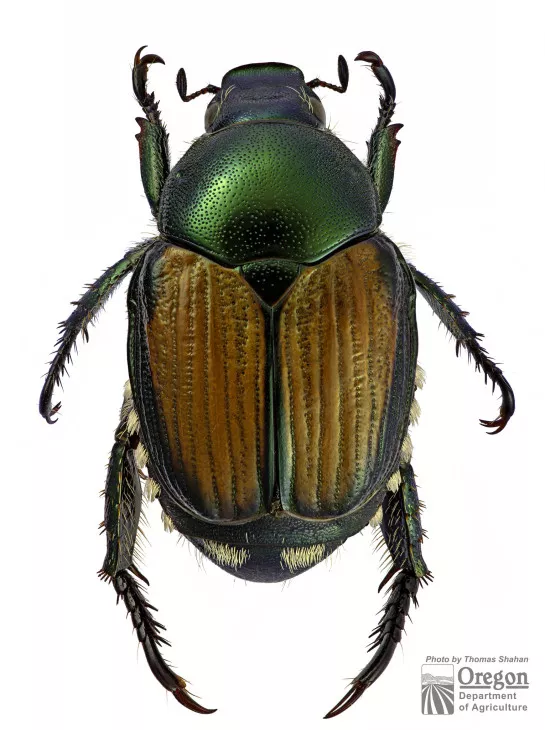
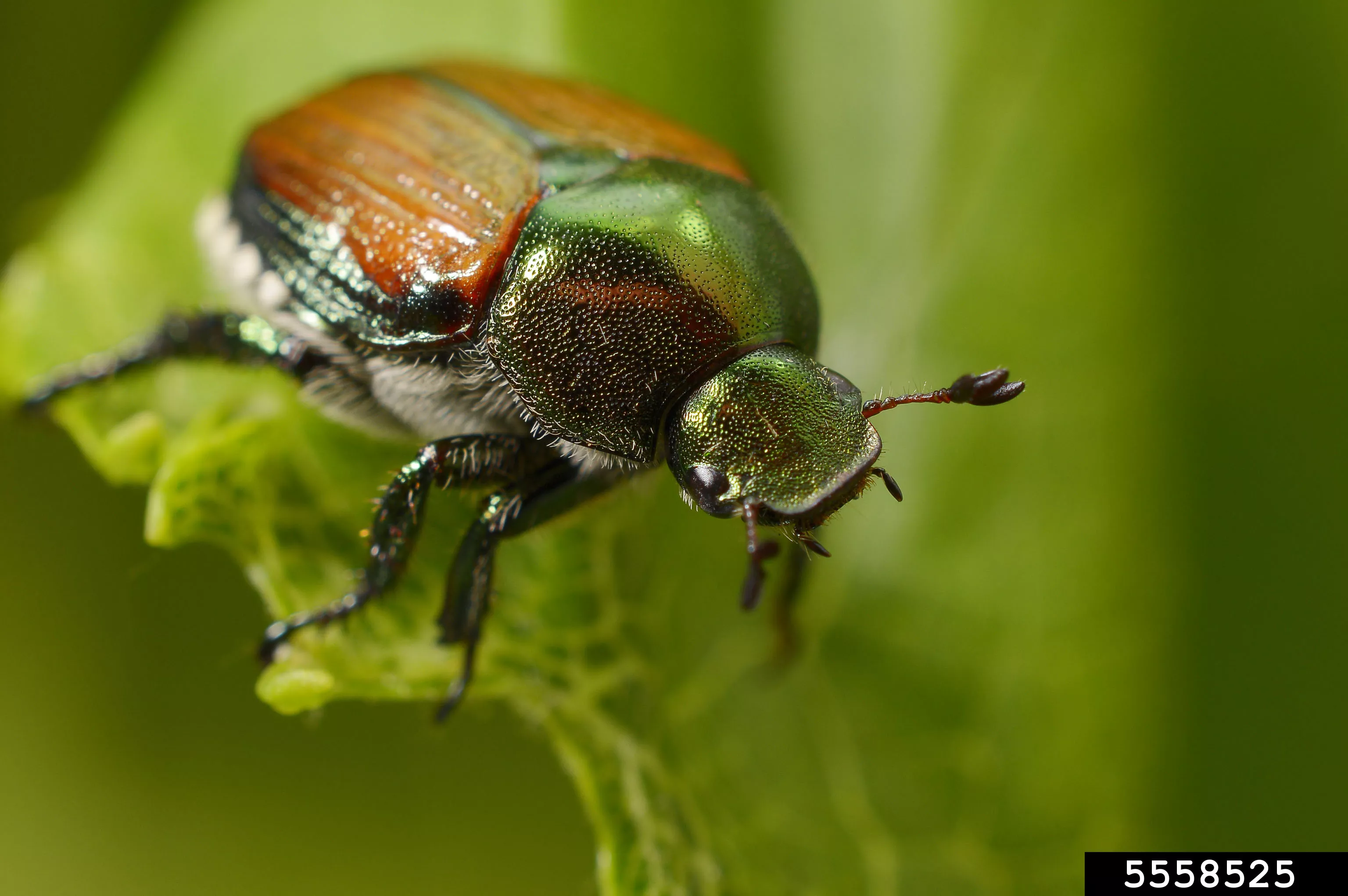
They emerge from the soil in June and are most actively. A Japanese beetle life cycle is completed in one year. Japanese beetles are metallic green with coppery-brown elytra hardened front wings and are about a.
However some adults may be found into September. Grubs live in turf roots fall winter spring emerging as adults in June for the cycle to begin again. Since then the beetle infestation is now firmly entrenched and spreading rapidly.
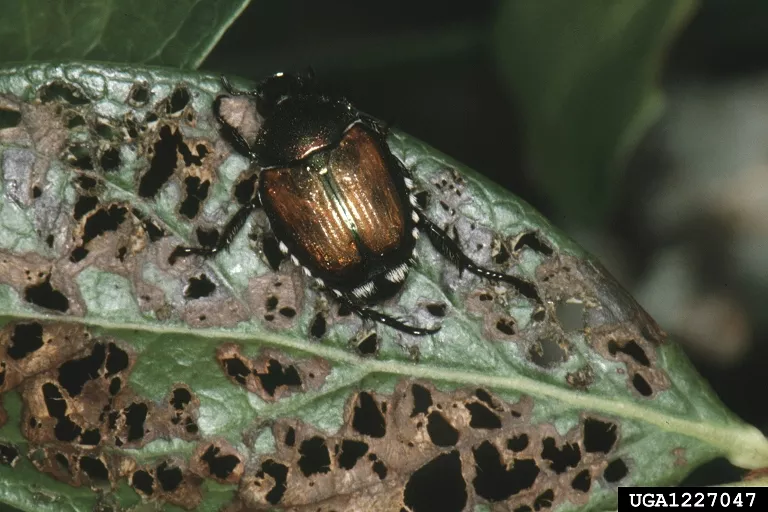
Adults males and females can be distinguished. For close to a century the Japanese beetle Popillia japonica has been one of the most seriously damaging insect pests of both turfgrass and landscape plants over a broad area of the eastern. Japanese beetles are attracted to over 300 plant species and will eat grass roots leaves.
In females the spine is rounded. Adults usually emerge from grass turf where they finished their underground life cycle in June. Japanese Beetle Fact Sheet from Colorado State University 5601 by Dr.
Japanese Beetle Life Cycle. Adults emerge from the soil in early June and starting feeding and mating on foliage and flowers of their host plants. After this spring feeding.
What is the life cycle of the Japanese beetle. The progressive life stages of the Japanese beetle during that period are egg. An adult Japanese beetle can feed on foliage fruits and flowers of over 300 species of plants in at least 79 plant families 2.
Adult beetles can be detected in traps until early September depending on weather conditions. Larvae and eggs of. Colorado was originally thought to be protected from invasive Japanese beetlePopillia japonicacolonization and establishment due to our semi-arid climate.
In mid-summer when the beetles are most abundant female beetles stop feeding each day just long enough to lay eggs a few inches down into the soil beneath our lawns. Life cycle and habits The entire life cycle requires about one year. Japanese Beetles in the Urban Landscape Purdue Extension.
A Japanese Beetle lives one year. Japanese beetles have a one-year complete life cycle from egg larva pupa adult. Japanese beetle has a life cycle that takes one year to complete.
The Japanese beetle Popillia japonica is a significant pest of landscape trees and shrubs vegetable and fruit crops and turfgrass in the eastern United States. The beetle was first discovered in Denver back in 2006. As adults Japanese beetles can be found feeding and mating on foliage and flowers of their host plants.
A Japanese beetle life cycle is completed in one year. Japanese beetles have a one-year life cycle adult beetles live for 30 to 45 days each summer eating mating and laying. The best way to control adult beetles is to make a preemptive strike in the spring well in advance of the adults emerging.
Japanese Beetle in Colorado The Japanese beetle is an invasive pest that was. Adults may begin to emerge from the soil in early June and are usually most abundant in early summer from late June through early August. Life Cycle and Plant Damage of the.
Japanese Beetle in Colorado The Japanese beetle is an invasive pest that was introduced into the eastern United States over 100 years ago. Japanese beetle has a one year life cycle. In June the grub turns into a pupa.
Adult beetles are most active in the heat of the day and are voracious feeders on ornamental and agricultural plant. The Japanese beetle was first introduced into Colorado in the early 1990s from nursery stock purchased in the mid-western United States.
Get Ready For Japanese Beetles Ross Tree Company Denver Colorado

Japanese Beetle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Tips On How To Control Japanese Beetles In Colorado

Tips On How To Control Japanese Beetles In Colorado

Japanese Beetles Are Here To Stay How Can We Fight Back
Colorado Garden Punch List Betty Cahill Japanese Beetle Spring Larvae Control

Bad Garden Bugs Identify Control Harmful Plant Insects Pictures

Colorado Garden Punch List Betty Cahill Japanese Beetle Blues
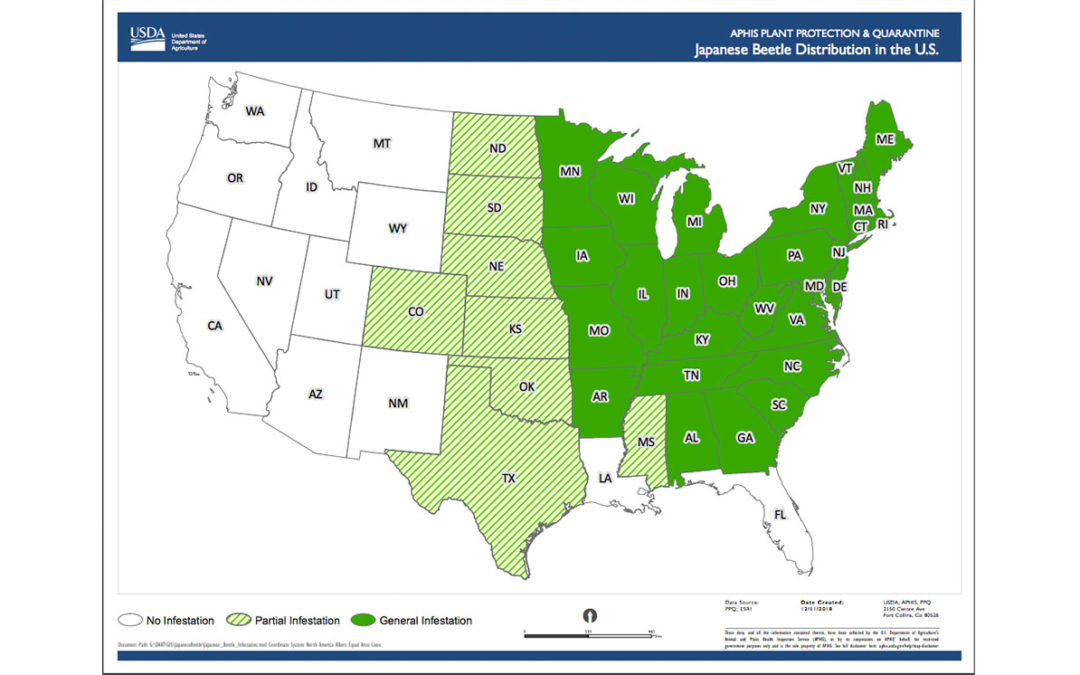
Prevention Mitigation And Management Of Japanese Beetle Department Of Agriculture

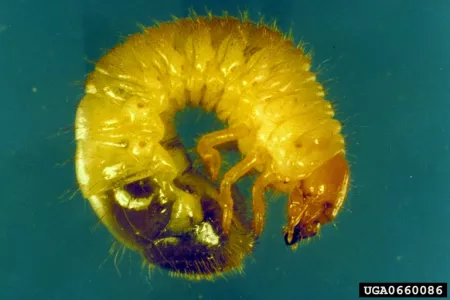
Japanese Beetle Larvae Popillia Japonica Entomology Today

Japanese Beetle Habitat Facts How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles Safer Brand

Colorado Garden Punch List Betty Cahill Japanese Beetle Update July August 2017

Japanese Beetle In Colorado Department Of Agriculture

Japanese Beetle In Colorado Department Of Agriculture

How To Survive The Coming Japanese Beetle Invasion Denver Public Library

Prevention Mitigation And Management Of Japanese Beetle Department Of Agriculture


